Product News
Understanding Electromagnetic Flow Meters
21 Nov 2024
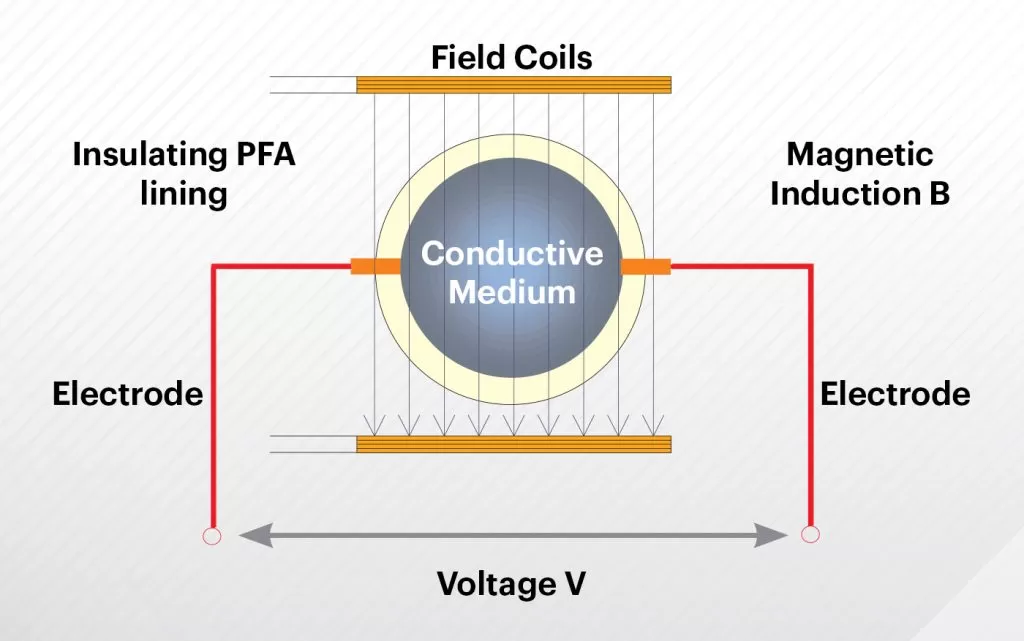
Electromagnetic flow meters, often referred to as mag meters or magnetic-inductive flow sensors, are devices designed to measure the flow of electrically conductive fluids by utilizing Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction. According to this principle, a voltage is generated when a conductive liquid moves through a magnetic field, which is directly proportional to the fluid’s velocity. This induction allows for precise flow measurements, making electromagnetic flow meters a popular choice in various industrial applications.
One of the key advantages of electromagnetic flow meters is their ability to measure both clean and dirty fluids, enhancing their versatility. For example, they can accurately measure wastewater or sludge, which is often challenging for other types of flow meters. Additionally, these meters can accommodate a wide range of fluid properties, such as varying temperature and viscosity, allowing them to be used effectively in different environments and industries.
How Electromagnetic Flow Meters Work
The operation of electromagnetic flow meters is based on the induced voltage (E), which can be mathematically expressed as E = KV, where K is a constant and V is the average fluid velocity. This relationship allows for the calculation of flow rates by measuring the voltage generated as the fluid passes through a magnetic field. Furthermore, electromagnetic flow meters can measure bi-directional flow, which adds to their utility in various applications.
Recent advancements in technology have led to the development of electromagnetic flow meters that can measure fluids with lower conductivity levels, broadening the types of fluids that can be accurately assessed. The measurement process involves placing electrodes in contact with the fluid, which facilitates the precise sensing of flow velocity and volume. Importantly, the design of electromagnetic flow meters is obstruction-free, reducing flow disturbances that can compromise measurement accuracy.
Applications of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Flow sensors find extensive application across multiple industries, including water treatment, food and beverage processing, chemical processing, and wastewater management. Their ability to handle slurries and highly corrosive fluids without obstruction makes them ideal for many industrial applications. For instance, in the food industry, they are used to monitor the flow of liquids to ensure accurate ingredient measurements while adhering to strict hygiene standards.
As technology evolves, the adoption of flow sensors in agriculture is also increasing, particularly for measuring irrigation flows and monitoring water usage. In addition, they play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry, where precise fluid management is essential for compliance with regulatory standards. Their use in cooling water systems further emphasizes their versatility, where they help monitor flow rates to improve energy efficiency.
Advantages of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
One notable benefit is their lack of moving parts, which results in lower maintenance costs and a longer service life compared to mechanical flow meters. They also offer high accuracy rates, achieving measurements with an accuracy of up to ±0.5% of the flow rate, which is superior to many other flow measurement technologies. This precision is particularly valuable in applications where accurate fluid measurement is essential.
Moreover, electromagnetic flow meters experience minimal pressure loss during fluid measurement, enhancing the overall operational efficiency of the systems they are integrated into. Their ability to measure flow in both directions provides significant operational flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. With a favorable turndown ratio of approximately 40:1, these meters can effectively measure a diverse range of flow rates, accommodating various operational demands.
Calibration and Maintenance of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
To ensure accurate measurements, regular calibration is crucial. This process is typically performed using water to validate the K factor, which can then be applied to other conductive liquids. Maintenance tasks also include ensuring proper grounding to prevent zero shifts and addressing potential issues such as air entrainment or electrode coating that can affect performance.
Installation guidelines for electromagnetic flow meters dictate the necessity of maintaining a full pipe and adhering to specific upstream and downstream straight pipe requirements to enhance measurement accuracy. Periodic verification checks are essential to confirm the functionality and accuracy of the flow meters over time. Users should also consider environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and electromagnetic interference, which may impact performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Users may encounter common challenges with electromagnetic flow meters, such as inaccurate readings resulting from air bubbles present in the fluid or issues near minimum velocity conditions. Troubleshooting solutions include selecting appropriate meters and ensuring stable flow profiles during installation. Regular monitoring of flow conditions and routine checks are important to maintain meter reliability and performance.
Another effective strategy to mitigate issues includes maintaining high flow velocities, which helps prevent air entrainment and ensures accurate measurements. Additionally, regular cleaning of electrodes is necessary to prevent any coating that could interfere with measurement accuracy. Being proactive in these maintenance and troubleshooting practices can significantly improve the reliability of electromagnetic flow meters in various applications.
Summary of the Importance of Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Electromagnetic flow meters play a critical role in various industries by providing accurate and reliable flow measurements. Their versatility in handling a wide range of fluid types, including conductive liquids in harsh environments, underscores their importance in modern industrial applications. For those interested in advanced hygienic instrumentation solutions, including innovative electromagnetic flow meters, Anderson-Negele offers products designed to meet stringent sanitary standards, enhancing process reliability and hygiene. For more information, visit Anderson-Negele.


Copyright © 2022 Anderson-Negele